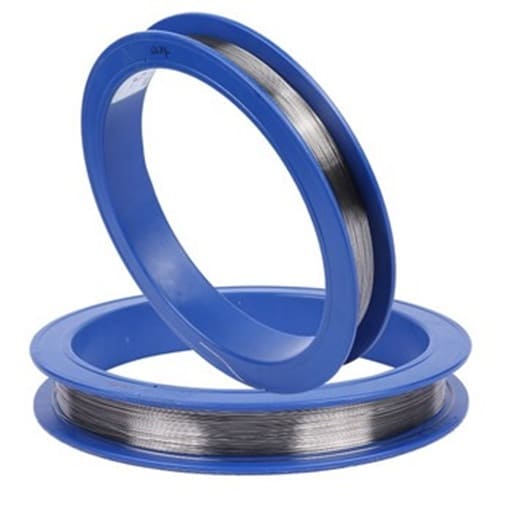
Tungsten Wire
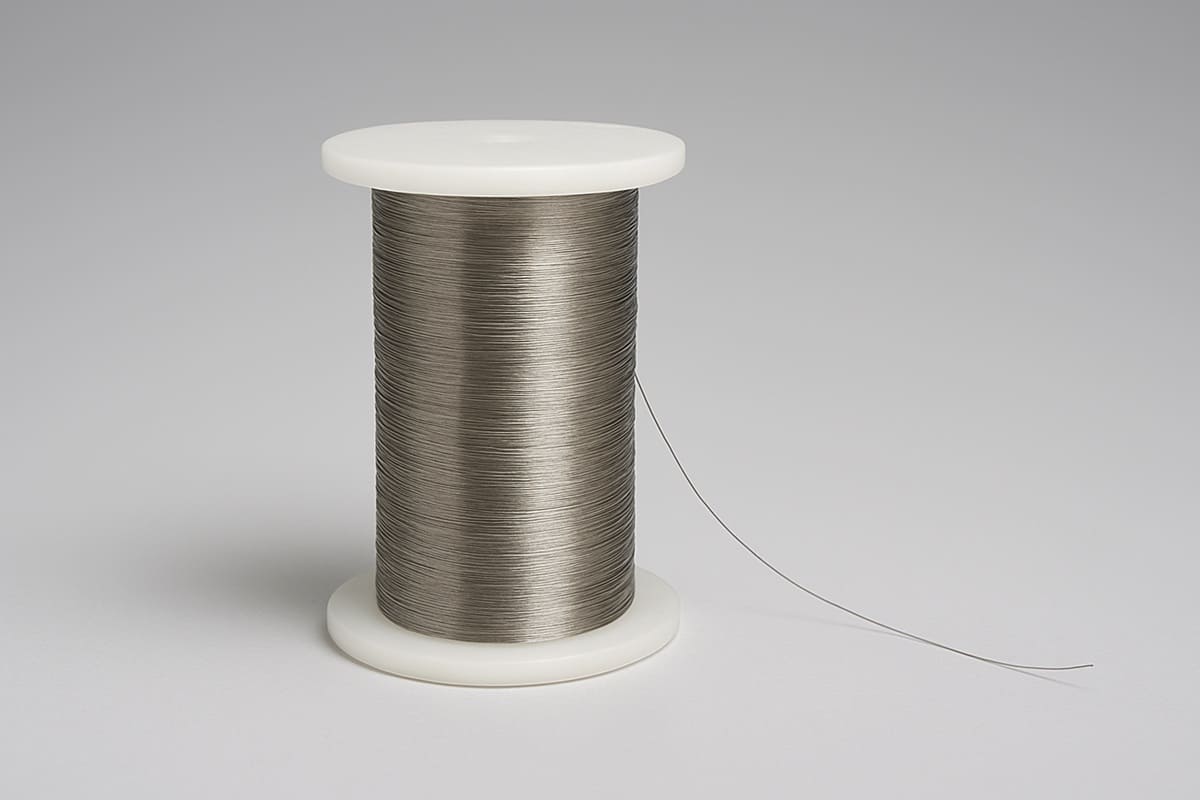

Tungsten Wire
Tungsten Wire offers an exceptionally high melting point, excellent high-temperature resistance, and good electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in electronics, lighting, vacuum technology, and arc welding. As a leading supplier and manufacturer of premium tungsten products, Shanghai Yuepeng utilizes advanced machining centers to produce high-precision tungsten and tungsten alloy foils, strips, and ribbons for a wide range of applications.
Tungsten Wire Data Sheet
| Reference: | HMWW1117 |
| Dimensions: | Diameter: 0.01-6 mm Length: customized |
| Material: | Tungsten and Tungsten Alloy (WRe3-26) |
| Purity: | 99%, 99.9%, 99.95%, 99.99%, 99.999% |
| Wire Type: | Round Wire, Flat Wire, or Square Wire |
| Product Form: | Straight, Coiled, or Spooled |
| Temper: | Annealed or Unannealed |
Tungsten Wire
Tungsten wire is forged and drawn from high-purity tungsten rods (up to 99.999%), offering exceptional electrical conductivity, a high melting point, and low thermal expansion, making it an ideal material for electrical applications. Shanghai Yuepeng provides customized solutions for diameter, length, wire type, and surface finish to meet specific requirements. We offer both Tungsten White Wire and Tungsten Black Wire, each suited for different industrial needs, ensuring optimal performance in a variety of applications.
Tungsten Wire Material Chemical Composition
| W (>%) | Chemical Content (<%) | |||||||||||
| 99.999 W1 | Fe | Ca | Be | Sn | Al | Ni | Zn | Sb | Pt | K | Ta | Na |
| 0.0001 | 0.00005 | 0.000005 | 0.000005 | 0.00005 | 0.00001 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00003 | 0.000005 | 0.0001 | 0.00005 | |
| Cr | Pb | As | Mg | Ti | Bi | Mo | Cd | Cu | Ba | Co | Mn | |
| 0.000005 | 0.00001 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.000005 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.000005 | 0.000007 | 0.00001 | 0.000005 | 0.000005 | |
| 99.99 W2 | Fe | Ca | Be | Sn | Al | Ni | Zn | Sb | Pt | K | O | Na |
| 0.0001 | 0.00045 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0040 | 0.0009 | |
| Cr | Pb | As | Mg | Ti | Bi | Mo | Cd | Cu | Ba | Co | Mn | |
| 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| 99.95 W3 | Fe | Ca | P | Sn | Al | Ni | N | Sb | Si | O | Pb | As |
| 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | |
| Mg | C | Bi | Mo | |||||||||
| 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |||||||||
Tungsten Wire Production Process
- Raw Material: Select high-purity tungsten powder.
- Powder Metallurgy: Mix with binder and compact into a green billet.
- Sintering: High-temperature sintering to remove the binder and increase density.
- Drawing: Draw the tungsten rod through the dies to form fine wires.
- Heat Treatment: Anneal to relieve stress and enhance properties.
- Surface Treatment: Clean and polish the surface.
- Cutting & Customization: Cut or customize according to requirements.
Tungsten Wire Processing Method
- Sintering
- Forging
- Rotary Forging
- Rolling
- Polishing
Tungsten Wire Surface Finish
Depending on the intended applications, tungsten wire has two main surface finishes as follows:
- Black: The surface is “as swaged” or “as drawn”, retaining a coating of processing lubricants and oxides.
- Cleaned: The surface is chemically cleaned to remove all lubricants and oxides.
Tungsten Wire Cut-Resistance
Tungsten Wire, with its exceptional hardness and cut resistance, is used in cutting tools, high-temperature components, and protective gear. Compared to stainless steel, tungsten offers superior hardness and cut resistance, and compared to PE, it performs much better against sharp tools, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
| Performance Comparison of Tungsten Wire, Stainless Steel Wire And PE | ||||
| Items | Tungsten Wire | Stainless Steel Wire | PE | |
| Universal | High Strength Type | |||
| Diameter | 13 – 35 um | 20 – 35 um | 33 – 50 um | 10 – 30 um |
| Tensile Strength | 3600 – 4000 N/mm2 | 4800 – 6000 N/mm2 | 1000 N/mm2 | 1000 – 1500 N/mm2 |
| Density | 19.3 g/cm3 | 19.3 g/cm3 | 7.85 g/cm3 | 0.91 g/cm3 |
| Vickers Hardness | 800 – 850 HV | 950 – 1000 HV | ≤ 210 HV | 50 – 70 HV |
| Pulling Force | 1% – 3% | 1% – 3% | 40% – 60% | 10% – 50% |
| Cut Resistance (A1-A9) | A5 – A9 | A5 – A9 | A3 – A4 | A2 – A3 |
| Flexibility (1-10) | 9 | 8 | 5 | 10 |
Tungsten Wire Applications
- Electronic Devices: Tungsten filaments are widely used to manufacture electronic components, including electron tubes, television picture tubes, semiconductor devices, and vacuum tubes. Their high melting point and excellent electrical conductivity make them essential in these applications.
- Lighting: Tungsten filaments are commonly found in incandescent and halogen bulbs due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and provide consistent illumination.
- Resistance Heating: Tungsten filaments are used in heating elements for electric stoves, ovens, and furnaces, thanks to their superior high-temperature stability.
- Vacuum Technology: Tungsten filaments serve as heating elements and electrodes in vacuum equipment, including electron microscopes, due to their durability and performance in low-pressure environments.
- Welding and Cutting: Tungsten filaments are key materials for electrodes in welding and cutting processes, such as TIG welding and laser cutting, because of their resistance to high temperatures and arc corrosion.
- Medical Equipment: Tungsten filaments are also utilized in medical devices, including X-ray tubes and imaging equipment, where their durability and performance are critical.
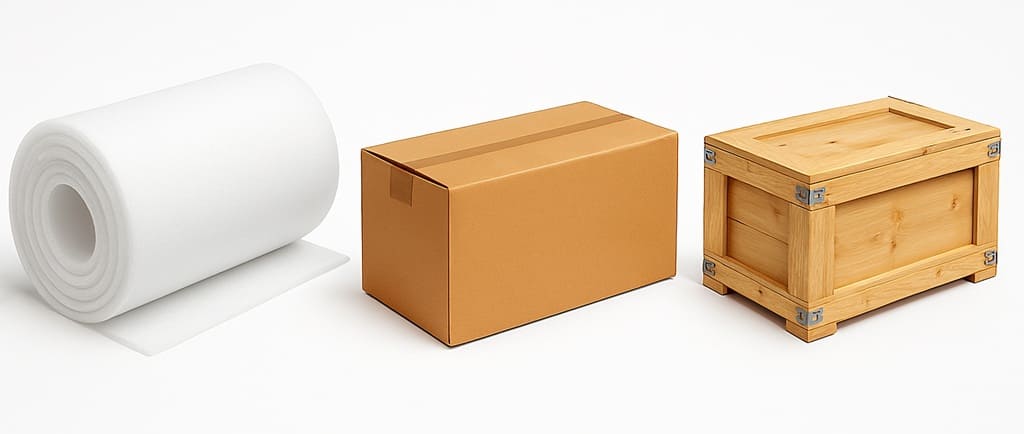
Tungsten Wire Packaging
The Tungsten Wire is carefully placed in wooden cases or cartons with additional support from soft materials to prevent any shifting during transportation. This packaging method guarantees the integrity of the products throughout the delivery process.

Tungsten Properties
Download
Get A Quote
We will check and get back to you in 24 hours.